Malondialdehyde (MDA)
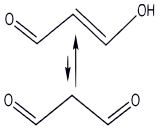
Malondialdehyde, MDA is a highly reactive three carbon dialdehyde produced as a byproduct of polyunsaturated fatty acid peroxidation and arachidonic acid metabolism. MDA readily combines with several functional groups on molecules including proteins, lipoproteins, and DNA. MDA-modified proteins may show altered physico-chemical behavior and antigenicity. Malondialdehyde is a highly reactive compound that is not typically observed in pure form. In the laboratory it can be generated in situ by hydrolysis of 1,1,3,3-tetramethoxypropane, which is commercially available. It is easily deprotonated to give the sodium salt of the enolate (m.p. 245 °C).Malondialdehyde reacts with deoxyadenosine and deoxyguanosine in DNA, forming DNA adducts, primarily M1G, which is mutagenic. The guanidine group of arginine residues condense with MDA to give 2-aminopyrimidines.
Organism species: Pan-species (General)
| PRODUCT TYPE | CATALOG NO. | PRODUCT NAME | APPLICATIONS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proteins | N/A | Recombinant Malondialdehyde (MDA) | Antigenic Transformation Customized Service Offer |
| Antibodies | N/A | Monoclonal Antibody to Malondialdehyde (MDA) | Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service Offer |
| N/A | Polyclonal Antibody to Malondialdehyde (MDA) | Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service Offer | |
| Assay Kits | N/A | CLIA Kit for Malondialdehyde (MDA) | CLIA Kit Customized Service Offer |
| N/A | ELISA Kit for Malondialdehyde (MDA) | ELISA Kit Customized Service Offer |
