High Density Lipoprotein (HDL)
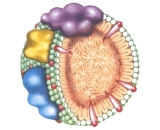
High-density lipoproteins (HDL) form a class of lipoproteins, varying somewhat in their size (8–11 nm in diameter), that carry cholesterol from the bodys tissues to the liver. About thirty percent of blood cholesterol is carried by HDL.HDL is the smallest of the lipoprotein particles. They are the densest because they contain the highest proportion of protein.
It is hypothesised that HDL can remove cholesterol from atheroma within arteries and transport it back to the liver for excretion or re-utilization—which is the main reason why HDL-bound cholesterol is sometimes called "good cholesterol", or HDL-C. A high level of HDL-C seems to protect against cardiovascular diseases, and low HDL cholesterol levels (less than 40 mg/dL) increase the risk for heart disease. When measuring cholesterol, any contained in HDL particles is considered as protection to the bodys cardiovascular health, in contrast to "bad" LDL cholesterol.
