Glucose Oxidase (GOD)
Gox; Glucose Oxidase Enzyme
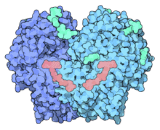
The glucose oxidase enzyme binds to beta-D-glucopyranose and aids in breaking the sugar down into its metabolites. GOx is a dimeric protein that catalyzes the oxidation of beta-D-glucose into D-glucono-1,5-lactone, which then hydrolyzes to gluconic acid. In order to work as a catalyst, GOx requires a cofactor, flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD). FAD is a common component in biological oxidation-reduction. Redox reactions involve a gain or loss of electrons from a molecule. In the GOx-catalyzed redox reaction, FAD works as the initial electron acceptor and is reduced to FADH2. Then FADH2 is oxidized by the final electron acceptor, molecular oxygen (O2), which can do so because it has a higher reduction potential. O2 is then reduced to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Glucose oxidase is found in honey and acts as a natural preservative. GOx at the surface of the honey reduces atmospheric O2 to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), which acts as an antimicrobial barrier.
