Lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC)
lysoPC; Lysolecithin; 1-Palmitoyl-sn-Glycero-3-Phosphocholine
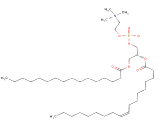
Lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC, 1-palmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) is an intercellular mediator regulating cell functions such as cell growth and immune response. Lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) is a bioactive proinflammatory lipid generated by pathological activities. LPC is also a major phospholipid component of oxidized low-density lipoprotein (Ox-LDL) and is implicated as a critical factor in the atherogenic activity of Ox-LDL. LPC is believed to play an important role in atherosclerosis and inflammatory diseases by altering various functions in a number of cell-types, including endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, monocytes, macrophages, and T-cells. LPC activates several second messengers -- including protein kinase C, extracellular-signal-regulated kinases, protein tyrosine kinases, and Ca(2+) -- implicating the engagement of transduction mechanisms in its observed actions.
