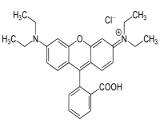
Rhodamine B is a chemical compound and a dye. It is often used as a tracer dye within water to determine the rate and direction of flow and transport. Rhodamine dyes fluoresce and can thus be detected easily and inexpensively with instruments called fluorometers. Rhodamine B is used in biology as a staining fluorescent dye, sometimes in combination with auramine O, as the auramine-rhodamine stain to demonstrate acid-fast organisms, notably Mycobacterium. Rhodamine B is tunable around 610 nm when used as a laser dye. Rhodamine B is being tested for use as a biomarker in oral rabies vaccines for wildlife, such as raccoons, to identify animals that have eaten a vaccine bait. The rhodamine is incorporated into the animal's whiskers and teeth. It is also often mixed with herbicides to show where they have been used.