Vanillylmandelic Acid (VMA)
Vanillyl Mandelic Acid
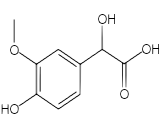
Moderately elevated VMA (vanillylmandelic acid) can be caused by a variety of factors such as essential hypertension, intense anxiety, intense physical exercise, and numerous drug interactions (including some over-the-counter medications and herbal products). Medications that may interfere with catecholamines and their metabolites include amphetamines and amphetamine-like compounds, appetite suppressants, bromocriptine, buspirone, caffeine, chlorpromazine, clonidine, disulfiram, diuretics (in doses sufficient to deplete sodium), epinephrine, glucagon, guanethidine, histamine, hydrazine derivatives, imipramine, levodopa , lithium, MAO inhibitors, melatonin, methyldopa , morphine, nitroglycerin, nose drops, propafenone, radiographic agents, rauwolfia alkaloids (Reserpine), tricyclic antidepressants, and vasodilators. The effects of some drugs on catecholamine metabolite results may not be predictable.
Organism species: Pan-species (General)
| PRODUCT TYPE | CATALOG NO. | PRODUCT NAME | APPLICATIONS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proteins | N/A | Recombinant Vanillylmandelic Acid (VMA) | Antigenic Transformation Customized Service Offer |
| Antibodies | N/A | Monoclonal Antibody to Vanillylmandelic Acid (VMA) | Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service Offer |
| N/A | Polyclonal Antibody to Vanillylmandelic Acid (VMA) | Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service Offer | |
| Assay Kits | N/A | CLIA Kit for Vanillylmandelic Acid (VMA) | CLIA Kit Customized Service Offer |
| N/A | ELISA Kit for Vanillylmandelic Acid (VMA) | ELISA Kit Customized Service Offer |
