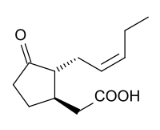
Jasmonic acid (JA) is derived from the fatty acid linolenic acid. It is a member of the jasmonate class of plant hormones. It is biosynthesized from linolenic acid by the octadecanoid pathway. The major function of JA and its various metabolites is regulating plant responses to abiotic and biotic stresses as well as plant growth and development.gulated plant growth and development processes include growth inhibition, senescence, tendril coiling, flower development and leaf abscission. JA is also responsible for tuber formation in potatoes, yams, and onions. It has an important role in response to wounding of plants and systemic acquired resistance. When plants are attacked by insects, they respond by releasing JA, which activates the expression of protease inhibitors, among many other anti-herbivore defense compounds.